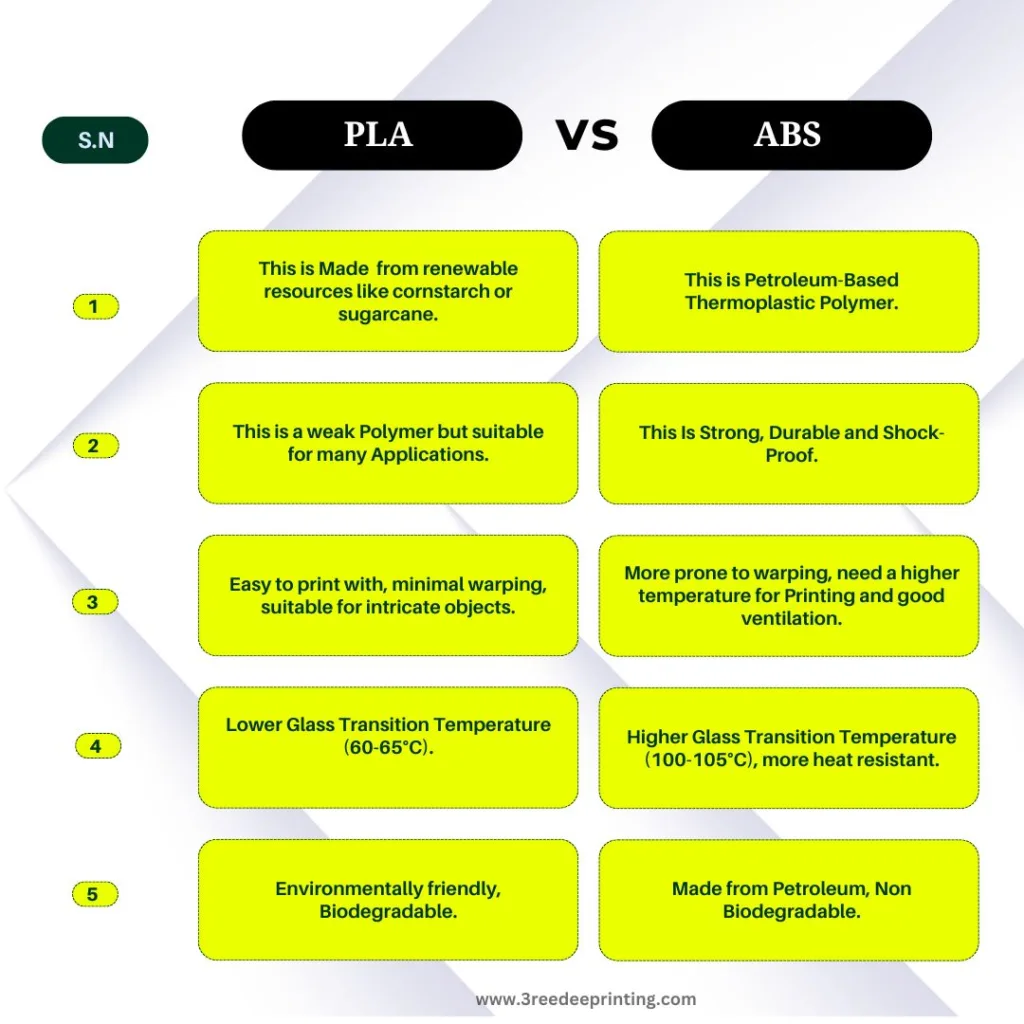
PLA is a type of Thermoplastic Polymer or Filament that is commonly used in 3D printing. Full form of PLA is Polylactic Acid, PLA is typically made from the sugars in corn starch, cassava or sugarcane. It is biodegradable and environmentally friendly compared to petroleum-based plastics (ABS). PLA is the best choice for educational settings, and prototyping applications because of its low tendency to warp and minimal shrinkage during cooling, making it suitable for printing complex and detailed objects, But it has some limitations such as lower heat resistance than other materials like ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene), which may restrict its to use in some applications.

What is ABS in 3D Printing?
This is a Strong, Durable and Shock-Proof Filament or Polymer. ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene) is a polymer made from Petroleum by combining these three products at one point by electrical induction. This process is called Styrene-Acrylonitrile-Butadiene-Conjugation and it produces a thermoplastic polymer called ABS. This is Non-Biodegradable or Compostable.
What is the Difference between PLA & ABS?
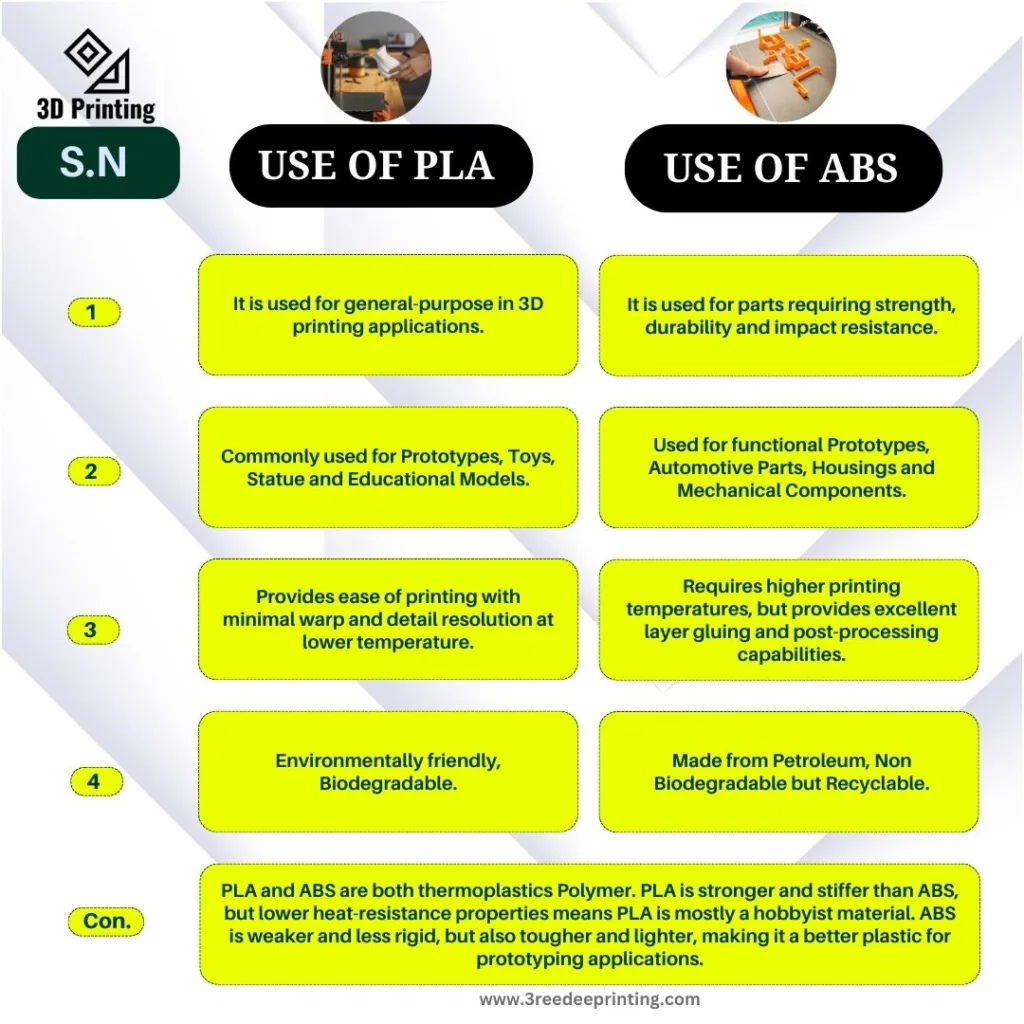
Use of PLA & ABS in 3D Printing
Types Of Polymer Or Filament in 3D Printing
There are several types of polymer or filaments commonly used in 3D printing-
- PLA (Polylactic Acid)
- ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene)
- Nylon
- PETG (Polyethylene Terephthalate Glycol)
- TPU (Thermoplastic Polyurethane)
- PVA (Polyvinyl Alcohol)
- ASA (Acrylonitrile Styrene Acrylate)
- PC (Polycarbonate)
Best Polymer or Filament for 3D Printing

